
All You Need to Know about Steel Frame Homes
Steel frame homes represent a departure from traditional residential construction methods by utilizing steel for structural support rather than the more conventional wooden frames. This approach offers a high degree of customization, enabling homeowners and architects to seamlessly integrate steel with a variety of other materials such as brick, concrete, or even wood veneers. This versatility allows for the creation of diverse architectural styles while still benefiting from the strength, durability, and other advantages that steel framing provides. Additionally, concealing the steel frame with these materials can help achieve specific aesthetic goals or blend the home seamlessly into its surroundings. While steel frame homes are generally resistant to rust due to protective coatings, they can still be susceptible to corrosion if the coatings are damaged or if the steel is exposed to moisture for extended periods without proper maintenance.
Advantage and Disadvantage of Having a Steel-Framed Home
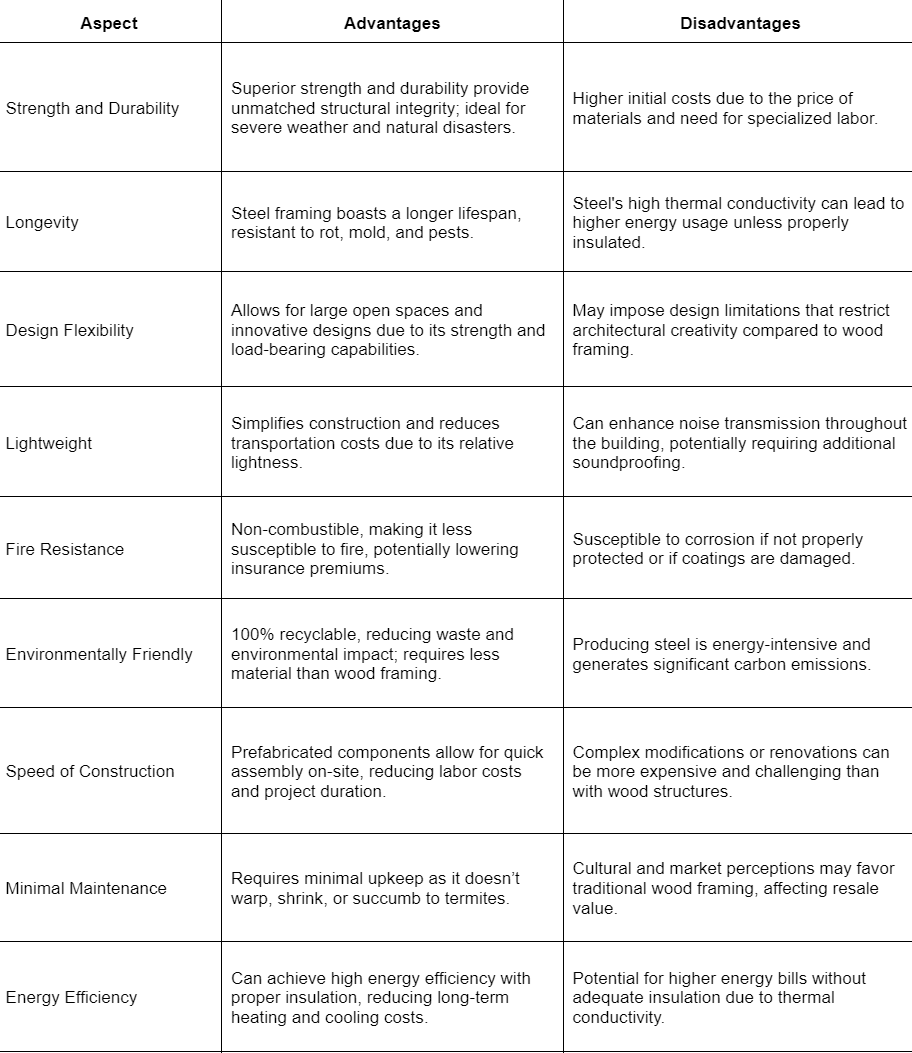

Here are the disadvantages of having a steel framed house:
Higher Initial Cost:
Building a house with a steel frame generally incurs higher upfront costs than those with traditional wood frames. This cost discrepancy stems from the price of raw steel materials and the need for specialized labor skilled in steel construction techniques. Although steel offers durability and longevity, the initial investment can be a significant barrier for some homeowners..
Thermal Conductivity:
Steel’s high thermal conductivity means that it can transfer heat and cold more efficiently than wood. This characteristic can lead to greater energy usage for heating and cooling, resulting in higher utility bills unless the structure is equipped with high-quality insulation. Homeowners must consider the added expense and effort to ensure proper insulation to mitigate this issue.
Design Limitations:
While steel frames provide strong structural support, they can sometimes impose restrictions on architectural design. The rigidity of steel may limit certain creative and aesthetic choices, particularly in complex designs that require more flexibility than steel can offer. This can be a disadvantage for architects and builders seeking to implement unique or intricate architectural features.
Noise Transmission:
Steel frames can enhance the transmission of sound vibrations throughout a building, potentially leading to noisier interiors unless specific sound-dampening materials are used. This can affect the overall acoustics of the home, requiring additional investments in soundproofing solutions to create a quiet and peaceful living environment.
Potential for Corrosion:
Although steel is durable and resistant to many forms of degradation, it is still vulnerable to corrosion under certain conditions. If the steel is not adequately treated with protective coatings, or if these coatings are compromised, rust can develop. This not only affects the structural integrity but also necessitates ongoing maintenance and repair to prevent significant damage.
Environmental Impact:
The production of steel is energy-intensive and associated with high levels of carbon emissions. This contributes to the broader environmental impact, including resource depletion and pollution. For those concerned with sustainable building practices, the ecological footprint of producing and using steel can be a significant drawback.
Complexity of Modifications:
Renovating or making modifications to a steel-framed house can be more complicated and expensive than alterations to a wood-framed structure. Cutting, welding, or altering steel beams requires specific equipment and expertise, potentially increasing the cost and duration of renovation projects.
Perception:
Cultural and market perceptions can also play a role in the disadvantages of steel-framed houses. Some potential buyers may prefer the traditional aesthetics and qualities of wood framing, viewing steel-framed houses as less cozy or inviting. This perception can affect resale value and marketability, particularly in regions where wood framing predominates.
Here are the advantages of having a steel framed house:
Strength and Durability:
Steel's superior strength and durability provide unmatched structural integrity, making it an ideal choice for areas prone to severe weather, earthquakes, and other natural disasters. The robust nature of steel ensures that structures are capable of withstanding harsh conditions without compromising their stability or safety.
Longevity:
Steel framing boasts a significantly longer lifespan than traditional wood framing. Its resistance to rot, mold, and pests such as termites means that steel structures can maintain their integrity over decades with minimal degradation, offering long-term benefits and reduced replacement costs.
Design Flexibility:
The inherent strength of steel allows for greater design flexibility in construction. Steel's ability to support heavy loads without the need for load-bearing walls opens up possibilities for large open spaces and ambitious, innovative architectural designs that would be challenging with other materials.
Lightweight:
Despite its strength, steel is relatively lightweight, which simplifies the construction process. The reduced weight lowers transportation costs and eases the handling and assembly of steel components on-site, facilitating a smoother and often faster construction process.
Fire Resistance:
Steel's non-combustible nature makes steel-framed houses less susceptible to fire, providing an additional safety advantage over traditional wood framing. This characteristic not only enhances the safety of the structure but can also contribute to lower insurance premiums.
Environmentally Friendly:
Steel is 100% recyclable, which minimizes its environmental impact by reducing waste. The ability to reuse steel contributes to a more sustainable construction practice. Additionally, steel frames often require less material by volume compared to wood frames, further diminishing the environmental footprint associated with resource extraction and processing.
Speed of Construction:
The prefabrication of steel framing components off-site allows for quick assembly on-site, accelerating the overall construction timeline. This efficiency in construction can lead to substantial savings in labor costs and reduce the overall project duration.
Minimal Maintenance:
The durability of steel reduces the need for frequent maintenance, saving homeowners significant time and money over the life of the building. Unlike wood, steel does not suffer from issues like warping, shrinking, or termite damage, making it an ideal low-maintenance option.
Energy Efficiency:
When combined with proper insulation techniques, steel-framed buildings can achieve high levels of energy efficiency. This capability helps in reducing heating and cooling costs, contributing to long-term savings and environmental sustainability.
Resistant to Mold and Mildew:
Steel does not provide a food source for mold and mildew growth, unlike wood. This resistance helps in maintaining better indoor air quality and reduces the potential health risks associated with mold and mildew, particularly in damp environments.
Comparing Wood and Metal Studs
Wood studs and metal studs each have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Wood studs are favored for their lower cost, availability, and ease of installation, but they are less durable and offer limited fire resistance compared to metal studs. In contrast, metal studs are stronger, more durable, and non-combustible, although they come with a higher initial cost and require specialized tools for installation. The choice between the two depends on factors such as budget, durability needs, and project requirements.
In choosing between the two it is also important to consider the cost, wood studs are generally cheaper upfront, while metal studs may offer long-term savings due to durability. The application, which depends on building codes, project requirements, and environmental conditions. And the maker’s skill level. Wood studs are easier for DIY projects, while metal studs may require specialized skills.
Here is the comparison of Wood Studs and Metal Studs:
 Wood Stud Framing
Wood Stud Framing
Construction experts commonly utilize wood stud framing for building foundational components in walls, floors, and roofs. It's essential to consistently opt for top-grade lumber when engaging in wood framing. Robust lumber ensures optimal structural integrity, and construction teams must diligently inspect for any signs of cracks or warping to assess quality.
Although framing methods may differ based on regional regulations and construction teams, the general process consists of the following steps:
Layout Preparation and Marking:
This phase involves meticulously planning and plotting the blueprint on the actual construction site or the framing area. Here, measurements are made to specify the exact location, dimensions, and orientation of all structural elements such as walls, doors, and windows. Tools such as measuring tapes, laser levels, and chalk lines are employed to ensure precision in marking the ground or subfloor for the upcoming structures.
Installation of Studs:
The installation begins with the placement of bottom and top plates followed by vertical wood studs. Each stud is measured, cut to the appropriate length, and fastened at regular intervals along the plates using nails or screws, depending on the structural requirements. Special attention is given to the structural bracing, typically installed at corners and junctions, to enhance the rigidity and earthquake resilience of the framework. This step ensures that the frame can withstand various stresses such as wind or seismic activity.
Inspection:
Once the wood studs are installed, a rigorous inspection is carried out. This includes checking the level and alignment of the studs using spirit levels and plumb lines. The inspection also focuses on the adequacy of fasteners and the robustness of bracings at critical points. Compliance with local building codes is verified with a special focus on safety standards, such as fire blocking, which prevents the spread of fire within wall cavities.
Metal Stud Framing
Similar to wood stud framing, metal studs serve as foundational elements in walls, floors, and roofs. Metal studs are known for their durability, resistance, and stability, which are superior to those of wood studs. Like wood studs, framing and installation techniques may vary, and adherence to regional regulations is essential. Framing with metal studs typically follows a similar process to wood stud framing.
Layout Planning and Marking:
Just as with wood, detailed planning is crucial. The layout for metal studs must be marked accurately on the work area to guide the precise placement of tracks (the metal equivalents of wood plates) and studs. The use of a laser level can be particularly effective in ensuring straight and accurate lines for the metal framework.
Cutting and Preparing Metal Studs:
Metal studs are cut to length using metal snips or a saw designed for metal cutting, ensuring each piece fits perfectly according to the planned layout. It’s crucial to deburr the cut edges to avoid any sharp edges that could pose safety risks during installation.
Installation of Metal Studs:
Metal studs are installed by securing them into the tracks at both the floor and ceiling. Screws or specialized metal framing fasteners are used, spaced at prescribed intervals to meet structural requirements. This method provides a sturdy framework suitable for supporting various types of wall finishes.
Adding Structural Components:
Structural integrity is further enhanced by installing additional metal components like braces, strapping, or bridging between studs, which help in resisting lateral loads and increasing the overall stability of the structure.
Inspection and Adjustment:
The final step involves a detailed inspection of the metal stud frame, focusing on alignment, the security of connections, and overall structural integrity. Adjustments are made as needed to ensure the frame is perfectly aligned and compliant with all applicable building codes, focusing on safety and durability.
Finishing Touches:
Once the framing is complete and meets all requirements, it can be prepared for subsequent construction phases, such as insulation, drywall installation, or exterior cladding.
Things you should know about Steel Framing
Since getting a steel framed house is a bit expensive obtaining a mortgage for a steel frame house is possible. Lenders generally prioritize the structural reliability of steel frame homes over the specific construction materials. However, it is advisable to discuss mortgage options with lenders to explore the full range of possibilities.
The longevity of a steel-framed house can vary based on several factors such as maintenance, environmental conditions, and construction quality. Generally, steel-framed houses are designed to last for many decades. With proper maintenance and care, they can endure well beyond 50 years. However, the specific lifespan of any individual steel-framed house will depend on factors such as regular upkeep, exposure to elements, and adherence to building standards.
Insulating a steel-framed house is possible. It offers numerous benefits, including improved energy efficiency, enhanced comfort, reduced noise transmission, and prevention of moisture-related issues like mold and mildew. Additionally, it contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing the home's carbon footprint. Overall, insulating a steel-framed house is a worthwhile investment for homeowners looking to improve comfort, energy efficiency, and durability.